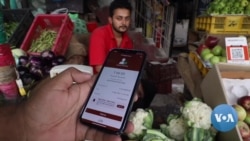
In the past year, there has seen a dramatic transformation in the way customers pay for their purchases in Banuri, a village in the Himachal Pradesh state of North India. Whether at a small grocery store or a street cart, instead of handing over cash, they use a simple system that involves scanning a code on a smartphone to make an online payment.
“Even if someone buys only half a kilogram of vegetables, he can pay digitally. We do the smallest of transactions,” said Nishant Sharma, a vegetable vendor in Banuri as he hands over a cauliflower to a customer that costs 75 cents. “It is much easier than handling cash.”
In recent years, a government initiative called “Digital India” has helped millions plug into new digital technologies as internet access expands to distant areas. One of them is a payments system that is transforming the way retail business is transacted in vast rural areas and small towns, where more than two thirds of India’s 1.4 billion people live.
Much like glitzy city stores, street vendors to small shops are making the switch to digital payments. But instead of credit or debit cards, they use India’s Unified Payment Interface popularly known as UPI. It is a payment system that involves no merchant fees and can be used for the smallest of transactions to make instant transfers across bank accounts. It was developed under the initiative of India’s Central Bank.
“It is the ease of the technology and overall reduction in transaction cost that has made this system popular. It takes place with the click of a button, it is cost-effective, and easy to manage,” said economist N.R. Bhanumurthy, Vice Chancellor at D.R. Ambedkar School of Economics University in Bengaluru. “It is certainly a huge transformation from what we did in the past and has changed the way we do business.”
Its expansion has also been helped by a massive push in recent years to bring more people into the banking system. More than 80% of adults now have bank accounts, compared to just one-third of adults some years ago. Affordable smartphones that cost as little as $50 are in the hands of about 750 million people. The COVID-19 pandemic, when cash transactions were discouraged, also prompted many to switch to digital payments.
“The Digital India Movement can bring about revolutionary changes in India and the lives of the common man," Prime Minister Narendra Modi said at an Independence Day address on Monday. According to the Indian leader, 40% of the real-time digital transactions made in the world now take place in India.
Whether in big towns, cities, or small villages, India’s retail sector is dominated by millions of small stores and shops, who for decades only did business in cash.
The speed and scale with which they are embracing the new payment system is evident in Banuri village. The owner of a chemist shop, Akhilesh Sharma, said about 70% of his customers pay online. It has eased his life.
“Whenever I open PhonePe or Google Pay app, all the transactions are done in my business account,” said Sharma. “In cash, I have to count the money at the end of the day, and it is a little long process. Then I have to go to bank and deposit the cash.”
Economists say digital payments boost business by facilitating transactions. Small town and village residents, especially younger customers, are also discovering the benefits of going cashless.
“I don’t have to worry about carrying money,” said Vikas Sharma, a resident of Palampur. “Earlier when I went to a crowded place, I worried about getting my wallet stolen. Now all I need is my phone.”
Digital transactions are just one of the benefits that the internet has brought people living in outlying areas. For older people such as a retired government employee, Romesh Dogra, the biggest benefit is connecting via video calls with his three daughters who live outside his district.
“I get energized daily when I talk to my grandchildren,” said Dogra, a retired official. “I can watch them growing up. Life has become good.”
There are still gaps to plug in — internet speeds can pose a challenge, especially in villages and small towns. And while the numbers of people with access to the internet have doubled to nearly 700 million in the last five years, millions are still not connected. But with rapid progress, it may not take long for India’s digital footprint to expand.